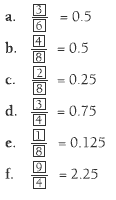This is a level 4 number activity from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 7 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (152 KB)
convert between fractions and decimals
calculator (optional)
This activity gives students practice at relating common fractions to decimals and vice versa. Students at this level should have experienced writing tenths and hundredths as a decimal and writing a decimal for any fraction expressed in tenths and hundredths. This will not necessarily mean that they can express other fractions as decimals.
Some sense of the relative size of fractions will be helpful in these situations, such as knowing that 3/5 is a little more than half or that 2/8 is the same as 1/4. Some examples are easily changed to a decimal, for example, 4/5 = 8/10, which is equal to 0.8. Alternatively, the students should think of a fraction as a division equation, for example, 4/5 means 4 ÷ 5 or
When the students are making up their own problems, you may want to limit the denominators that they use. They could use calculators to explore possibilities for creating equations.
As a variation, the students could use the inequation symbols > < in these statements, or you could give them some examples for which they have to supply the correct operator, < or >. For example, 3/4 5/8, 2/3 3/5, and so on.
Answers to Activity
1.
2. Answers will vary.