This is a level 4 number link activity from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 7 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (200 KB)
explore the order of operations in problems
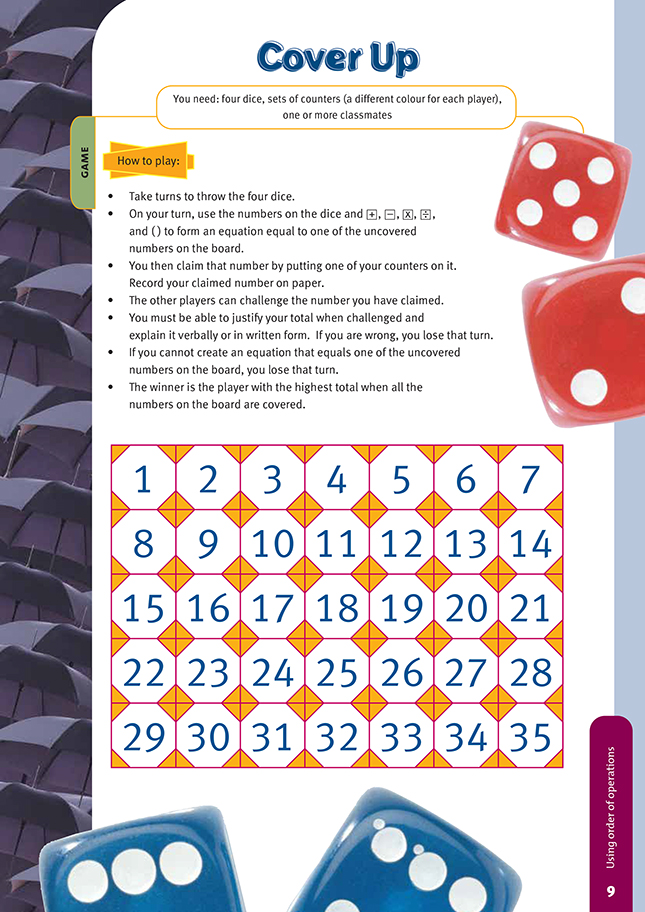
Sets of counters (a different colour for each player)
4 dice
FIO, Link, Number, Book Three, Cover Up, page 9
1 or more classmates
Clear, coloured counters are ideal for this game, in which the students use their basic facts along with their understanding of the order of operations. They need a good understanding of the order of operations conventions.
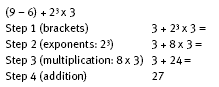
The acronym BEDMAS is often used to help students remember the order of operations. Each letter stands for an operation, and the order of letters in the acronym is the order in which to perform the operations.
In BEDMAS, B refers to anything inside brackets in the equation. E refers to exponents, that is, powers, square roots, and so on. D and M refer to division and multiplication, including finding the percentage of numbers. Division and multiplication are treated together and completed as they are encountered in the equation going from left to right. A and S refer to addition or subtraction, which are treated together and completed as they are encountered in the equation going from left to right.
An example is:
Some calculators follow these conventions for ordering operations, and some calculators do not. Have the students check out several calculators and decide whether they follow these conventions. You could use something like 8 – 2 x 3 = as a quick test. If 8 – 2 x 3 = 18, the calculator does not follow the normal conventions. If 8 – 2 x 3 = 2, it does. A more advanced test is the equation above.
Answers to Activity
Game
A game using order of operations