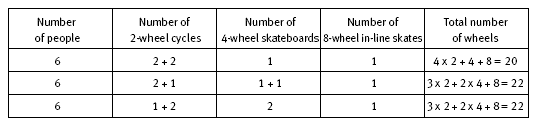This is a level 4 algebra strand link activity from the Figure It Out series.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (209 KB)
use a table to find a linear relationship
FIO, Link, Algebra, Book One, Which Wheels Where? page 20
In this activity, students work with simple linear equations in order to draw conclusions about the number and types of skatepark users. Encourage the students to approach the questions in a systematic way rather than guessing and checking solutions.
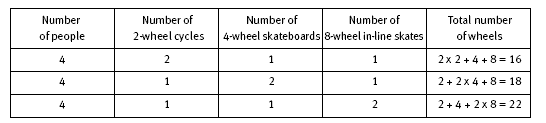
In question 1, recording in a systematic way in a table may help the students to reason logically. In question 1a, the students should reason that because there are just 4 people involved and at least 1 must be a cyclist, 1 a skateboarder, and 1 an in-line skater, there are three possibilities. There could be 2 cyclists, or 2 skateboarders, or 2 in-line skaters. The table below shows the three possible solutions.
In question 1b, the total number of people involved is 6. Note that the data in the first row in the table above can be modified in two ways, represented by the first two rows in the table below. The second row in the table above can be modified to produce the third row in the table below. This produces the same set of riders
as the second row in the table below, so effectively there are only two possibilities. Changes made to the numbers in the third row in the first table would not meet the new conditions.
The number of wheels of each type can then be calculated by considering the number of users of each type of transport as listed in the table.
In question 1c, David and Francie have different types of wheels. This situation is represented by the data in the second row in the table above, where either David or Francie rides a cycle and the other rides a skateboard.
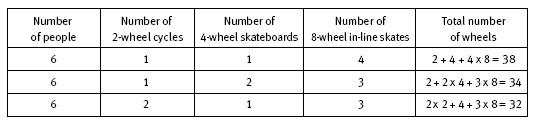
In question 2, using a table in a systematic way will ensure that the students will consider all the possibilities. In such tables, a good strategy is to initially consider the machine with the greatest number of wheels, in this case, the in-line skates. The students should make the number of in-line skates as large as possible and then systematically consider other possibilities.
The students do not need to go beyond the data in the first row of the table because different combinations of riders with fewer sets of in-line skates will always include fewer than 38 wheels.
Answers to Activity
1. a. There are three possible answers:
16 wheels (2 people with 2 cycle wheels each, 1 person with 4 skateboard wheels, and 1 person with 8 in-line skate wheels);
18 wheels (1 person with 2 cycle wheels, 2 people with 4 skateboard wheels each,
and 1 person with 8 in-line skate wheels);
22 wheels (1 person with 2 cycle wheels, 1 person with 4 skateboard wheels, and
2 people with 8 in-line skate wheels each).
b. There are two possible answers:
20 wheels (4 people with 2 cycle wheels each, 1 person with 4 skateboard wheels, and 1 person with 8 in-line skate wheels);
22 wheels (3 people with 2 cycle wheels each, 2 people with 4 skateboard wheels each, and 1 person with 8 in-line skate wheels).
c. 22 wheels. (An extra cyclist and an extra skateboarder added to the first option in 1a gives the second option in 1b above.)
2. 1 cyclist, 1 skateboarder, and 4 in-line skaters