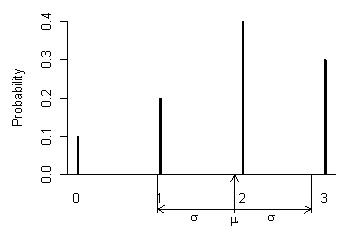
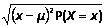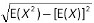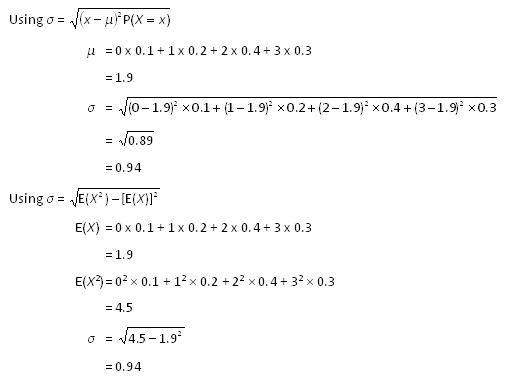Thanks for visiting NZMaths.
We are preparing to close this site and currently expect this to be in June 2024
but we are reviewing this timing due to the large volume of content to move and
improvements needed to make it easier to find different types of content on
Tāhūrangi.
We will update this message again shortly.
For more information visit https://tahurangi.education.govt.nz/updates-to-nzmaths