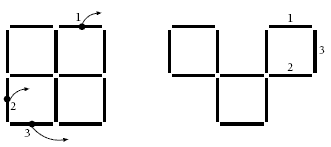This is a Level 2 Geometry activity from the Figure It Out Series.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (154 KB)
make shapes on a geoboard.
A geoboard sheet
FIO, Level 2-3, Geometry, Shaping Up, page 6
A rubber band
Rods
Activity One
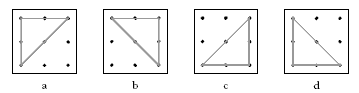
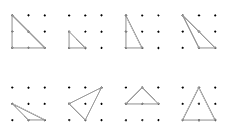
The main purpose of this activity is to get students to classify triangles and thereby broaden their knowledge about the properties of triangles. There are a limited number of different triangles that can be made on a 3 x 3 geoboard. Students may find it difficult to see a reflection or rotation of a given triangle as being the same triangle.
It can be very helpful to put copies of the geoboard on a transparency to show on an overhead projector. For example:
Triangles a, b, c, and d are congruent and can be mapped onto one another by rotation.
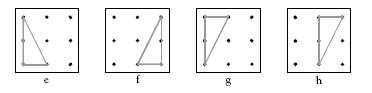
Triangles e, f, g, and h are all congruent and can be mapped onto each other by combinations of reflection (for example, e <–> f), rotation (for example, f <–> g), or translation (for example, g <–> h):
Asking students to come up to the projector and fit one triangle onto another by flipping, turning, or shifting is a good way to test the uniqueness of particular triangles.
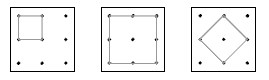
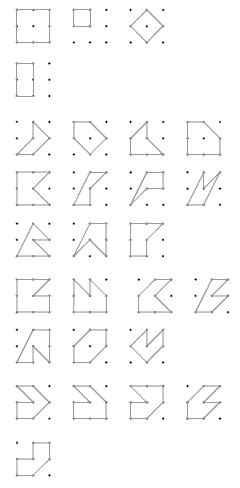
The purpose of the table in question 2 is not to make the problem more difficult but to get students to organise their results and classify the shapes they find. For example, the three different squares that are possible are also types of rectangles.
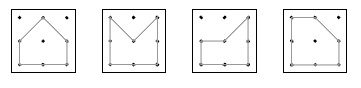
The shapes below are all examples of pentagons:
Activity Two
A useful strategy to begin the problems in this activity is to imagine the size that the target squares could be. Given the starting figure, they can only be of the sizes:
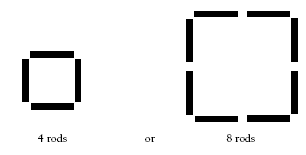
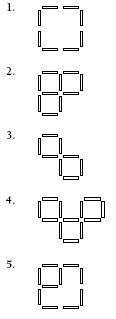
Use rods or matchsticks for these exercises. Question 1 involves leaving only one square after removing four rods. To leave a smaller square of , students would have to take away more than four rods. Therefore, the target square in this question must be
. To achieve this, students will take away more than four internal rods. The other problems in questions 2–5 can be solved using similar reasoning.
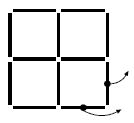
Question 2:
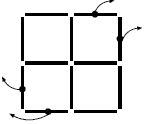
Question 3:
Question 4:
Question 5:
Answers to Activities
Activity One
1. Some possible answers are:
2. Some possible answers are:
Activity Two