The purpose of this activity is to support students in scaling fractions to a percentage when the denominator is a factor or near factor of one hundred.
- Connecting cubes
- Paper and pens
- Calculators
- Create a stack of 10 cubes, four yellow and six blue.
What fraction of this stack is yellow? What fraction is blue?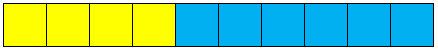
Use this easy example to show how a double number line can be used: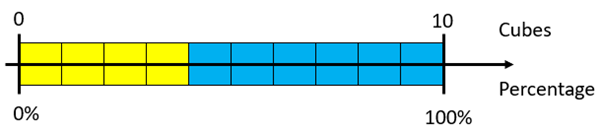
What percentage is each cube worth?
If each cube equals 10%, what percentage are yellow and blue?
Highlight the scaling of each fraction, 4/10 and 6/10, through multiplying both numerator and denominator by ten.
4/10 = 40/100 = 40% and 6/10 = 60/100 = 60%.
- Use other bases to develop the scaling idea. Allow students to work in groupings that will encourage peer scaffolding and extension, as well as productive learning conversations. Consider your students' fraction and multiplication basic facts knowledge when setting these problems. You might also introduce relevant te reo Māori kupu, such as ōrau (percent).
- Make a stack of 9 yellow and 11 blue cubes.
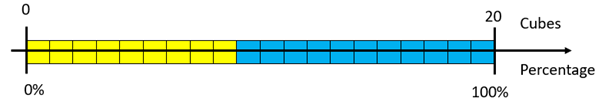
What percentage is each cube worth? (5%)
If each cube equals 5%, what percentage are yellow and blue?
Highlight the scaling of each fraction, 9/20 and 11/20 through multiplying both the numerator and denominator by five.
9/20 = 45/100 = 45% and 11/20 = 55/100 = 55%.
- Make a stack that has 14 yellow and 11 blue cubes.
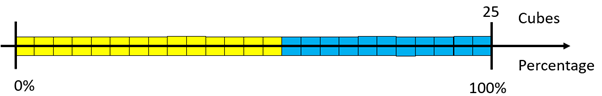
What percentage is each cube worth? (4%)
If each cube equals 4%, what percentage are yellow and blue?
Highlight the scaling of each fraction, 14/25 and 11/25 through multiplying both numerator and denominator by four. 14/25 = 56/100 = 56% and 11/25 = 44/100 = 44%.
- Make a stack that has 13 yellow and 27 blue cubes.
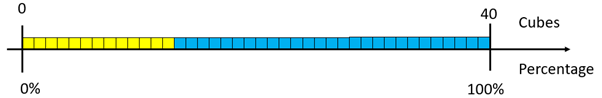
What percentage is each cube worth? (2.5%)
If each cube equals 2.5%, what percentage are yellow and blue?
Highlight the scaling of each fraction, 13/40 and 27/40 through multiplying both numerator and denominator by two and one half. 13/40 = 32.5/100 = 32.5% and 27/40 = 67.6/100 = 67.5%.
- Make a stack of 9 yellow and 11 blue cubes.
Next steps
- Increase the level of abstraction with the aim of students using symbolic form. Start by using stacks of discrete numbers of cubes, before progressing to schematic diagrams with only the number of cubes given:
![]()
In symbolic form express the fractions as 27/50 and 23/50. This can be converted to percentages by scaling to 100. 50 multiplied by two equals 100 so 27/50 = 54/100 = 54% and 23/50 = 46/100 = 46%.
- Consider which denominators make scaling a useful strategy. Begin by finding the factors of 100. Denominators of 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25 and 50 are therefore ideal for scaling. A few other denominators can be a manageable as well. For example, 8 x 12.5 = 100 so a base of eight is alright as well. 40 x 2.5 = 100 so a base of 40 is also viable.