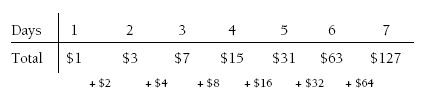These are a level 3 number, geometry, and measurement problems from the Figure It Out series.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (234 KB)
use additive strategies to solve problems (Problems 1 and 4)
arrange 3 dimensional pieces to make a cube (Problem 2)
solve problems involving addition and capacities (Problem 3)
Problem One
Students may express the problem as a series of calculations. For example:
$1 x 2 = $2 $2 x 2 = $4 $4 x 2 = $8 $8 x 2 = $16
$16 x 2 = $32 $32 x 2 = $64
$1 + $2 + $4 + $8 + $16 + $32 + $64 = $127
Alternatively, they may express the solution as progressive sums:
Extend the problem by asking “How much would Tàne get if he worked one more day (eight in total), … two more days … three more days?”
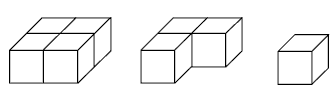
Problem Two
Students will need isometric dot paper and multilink cubes to create their own cube puzzles. For example:
Students may like to make shapes other than a cube block with the three pieces and draw the shape for a partner to build.
Problem Three
Students may need to see the glass of water poured into a 2 litre bottle. This will give them a benchmark to estimate from.
Since 2 litres is equivalent to 2000 millilitres, there will be space for ten 200 millilitre glasses. The bottle will hold a little more than this because it is not completely full of soft drink when it is bought.
The 1.5 litre bottle will hold at least 1500 millilitres, so seven and a half glasses of water will fit in it.
A variety of household containers could be used to find out the students’ ability to estimate capacity.
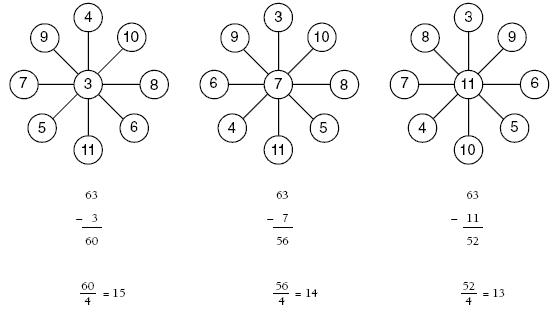
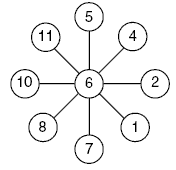
Problem Four
Students will need to look for four pairs of numbers with the same total to balance the wheel. This will mean matching a low number with a high number, for example 1 and 11, 2 and 10, etc.
In this problem, the median number, 6, is pivotal in achieving the balance needed. To extend the problem, give the students the numbers 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 to place in the circles. This extension will have three solutions:
Answers to Problems
1. a. $127
b. Answers will vary, but his mother probably won’t agree.
2. a. Possible solutions:
.gif)
b. Teacher to check
3. a. 10 glasses
b. 7.5 glasses
4.