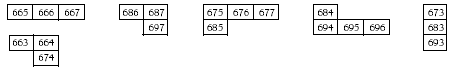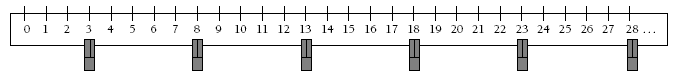Activities Two and Three are level 2 number activities from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 5 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (194 KB)
sequence numbers
skip count on a calculator
FIO, Level 2-3, Number, Happy Hundreds, page 1
Coloured pencils
Calculator
Activity One
Some students may need to re-enact what Jodi did and write the numerals on a set of cards. Most are likely to write list of numbers and find the middle number, as below..gif)
Some students will recognise that the numbers are answers to the nine times table (multiples of nine). These numbers also have a digital sum of nine, for example, 2 + 7 = 9 in the case of 27. Other students may observe that the numbers form a diagonal path on the hundreds board. (A copymaster for a hundreds board is provided at the back of this booklet.)
Students should be encouraged to perform the same task with other sets of numbers, for example, multiples of five: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, …
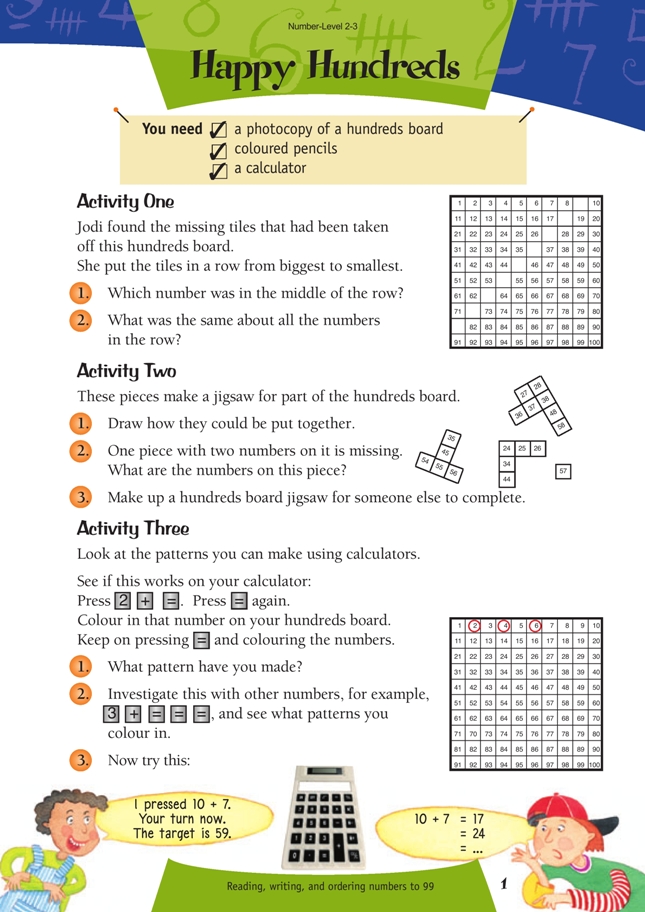
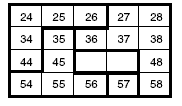
Activity Two
Some students may need to see a complete hundreds board. Useful prompts for students might be:
“What patterns can you see in the numbers?”
“Which number is smallest/largest?”
“Which numbers are likely to be in the middle of the jigsaw?”
Students could make models of the pieces out of squared paper and manipulate them to find the solution.
Rather that providing students with copies of hundreds boards to work with, encourage them to make their own jigsaws and write in the numbers.
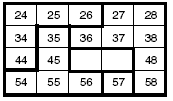
One method of drawing a jigsaw is illustrated here:
As an extension, a jigsaw could be made from pieces in a 601–700 board. For example,
Activity Three
For this activity, you will need to check the kinds of calculators students are using. Simple calculators seem to work as indicated in the activity, but others need two + + to achieve the desired result (that is, 2 + + = = = ). Some scientific calculators will not be able to be used for this activity.
In question 3, you will need to check whether the students’ calculators add seven, as in the illustration, or ten, which would need a different target.
The constant capability of a four-function calculator is activated whenever an operation is keyed in followed by the = button. From that point on until the button is pressed, the same operation will be performed on the window number each time = is pressed. For example, + 2 = = = = = … generates the multiples of two. These form a pattern of columns on a hundreds board.
You should ask students to explain why that occurs. Since each row of ten is divisible evenly by two, each row will have the same sequence of counters. With + 3 = = = = …, which generates the multiples of three, the pattern is diagonal. This is because each row is divisible by three with a remainder of one, which means the sequence is one to the left (one advanced) compared with that on the previous row.
Question 3 encourages students to apply skip counting. Many students will find pegs on a number line a useful visual model of the process. For example, starting with 3 + 5 … and pressing = until 28 is in the window could be modelled as:
Answers to Activities
Activity One
1. 45
2. Possible answers:
They are all divisible by 9.
The digits all add to 9.
The difference between each number is 9.
Activity Two
1.
2.
3. Answers will vary.
Activity Three
1. Answers will vary, for example, vertical lines, multiples of two.
Note: Check the calculators the students are using to make sure this procedure works.
The activity may need to be modified for different calculators.
2. Answers will vary.
3. 17, 24, 31, 38, 45, 52, 59
On some calculators: 17, 27, 37, 47, 57