Solve problems using a combination of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division mental strategies.
Solve multiplication and division problems by using place value.
Solve multiplication and division problems by using tidy numbers.
Number Framework Stage 6 and 7.
Place value materials (beans or place value blocks or play money)
Post-its (optional)
Using Materials
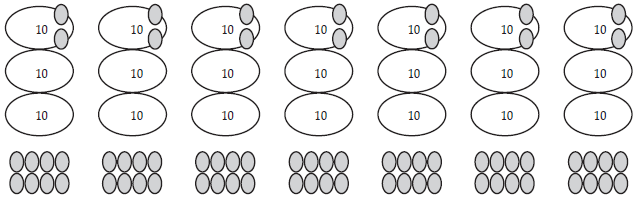
Problem: “Each container has 38 beans (cubes or dollars). There are seven
containers. How many beans are there altogether?”
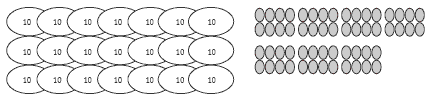
Set up a materials model of the problem:
.gif)
Ask the students to think of a way to solve the problem. Get them to explain their
strategies. Move place value materials to model each strategy. These strategies might
include:
“Adding two to each 38 to make seven forties. That makes 280. Take the seven twos away. That makes 266.”
Or: “Seven thirties are 210. Seven eights are 56. Two hundred and ten and 56 is 266.”
Provide other examples using materials. Focus on the sharing of strategies and how
they relate to actions on the materials. For example: 8 x 26 might be solved as
(8 x 20) + (8 x 6) (using place value)
or (8 x 25) + 8 (using rounding and compensating [tidy numbers])
or (8 x 30) – (8 x 4) (using rounding and compensating [tidy numbers])
or 2 x 26 = 52, 2 x 52 = 104, 2 x 104 = 208 (multiplying and doubling).
3 x 27 might be solved as (3 x 20) + (3 x 7) or (3 x 30) – (3 x 3) or (3 x 25) + (3 x 2) or 9 x 9. Note that the last strategy is proportional adjustment and involves separating each set of 27 into three nines.
Using Imaging
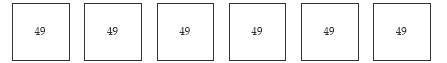
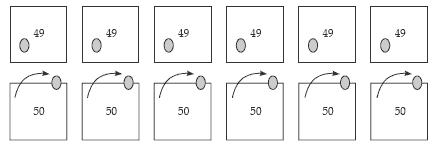
Shielding: Pose similar problems and mask the place value materials with ice cream
containers. Write the numbers involved on stickies, for example, 6 x 49 = □ can be
modelled as:
Ask the students to image what is happening to the materials as others explain their
strategies. For example, 6 x 49 = (6 x 50) – (6 x 1) (rounding and compensating).
Other examples of problems might be:
5 x 68 = ? 4 x 97 = ? 9 x 44 = ? 3 x 99 = ? 7 x 26 = ?
Using Number Properties
Increase the size of the numbers involved, thereby requiring the students to
abandon imaging in favour of noticing number properties.
Examples might be:
8 x 179 = ? 3 x 66 = ? 4 x 348 = ? 9 x 83 = ? 6 x 78 = ?
6 x 333 = ? 486 x 5 = ? 4 x 275 = ? 7 x 306 = ? 5 x 999 = ?
Independent Activity
To develop their estimation strategies with multiplication, students should play
Multiplication Roundabout (Material Master 6–6(b)).