The purpose of this activity is to support students in solving subtraction problems (taking away) with three-digit numbers, which involve either decomposing and renaming one ten as ten ones, or one hundred as ten tens.
- Place Value People (a paper representation of hundreds, tens, and ones to be used by students)
- Scissors
- Calculators
- Three-column place value boards
- Pose initial problems with two-digit whole numbers, before progressing to problems with hundreds, tens, and ones. Use the context from the diagnostic question (or alter this to better reflect the interests and backgrounds of your class) and alter the numbers. Restrict the renaming of digits to one place (column).
There are usually 71 students at the school. 28 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today? - Demonstrate subtracting tens first, before "going back through ten" (i.e. 71 - 20 - 1 -7) on an empty number line.
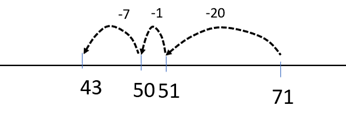
- Demonstrate using the decomposition algorithm by ‘decomposing’ one ten as ten ones. This allows you to subtract a larger number (e.g. 11) from a smaller number (e.g. 1), using the columns of a place value table. In this example, one group of ten (in the tens column) is decomposed and moved as ten ones in the ones column. Subsequently, the number 71 can be renamed as "sixty eleven" and written as 60 + 11 or 60 + 10 + 1. The diagrams below show what the process looks like with Place Value People.
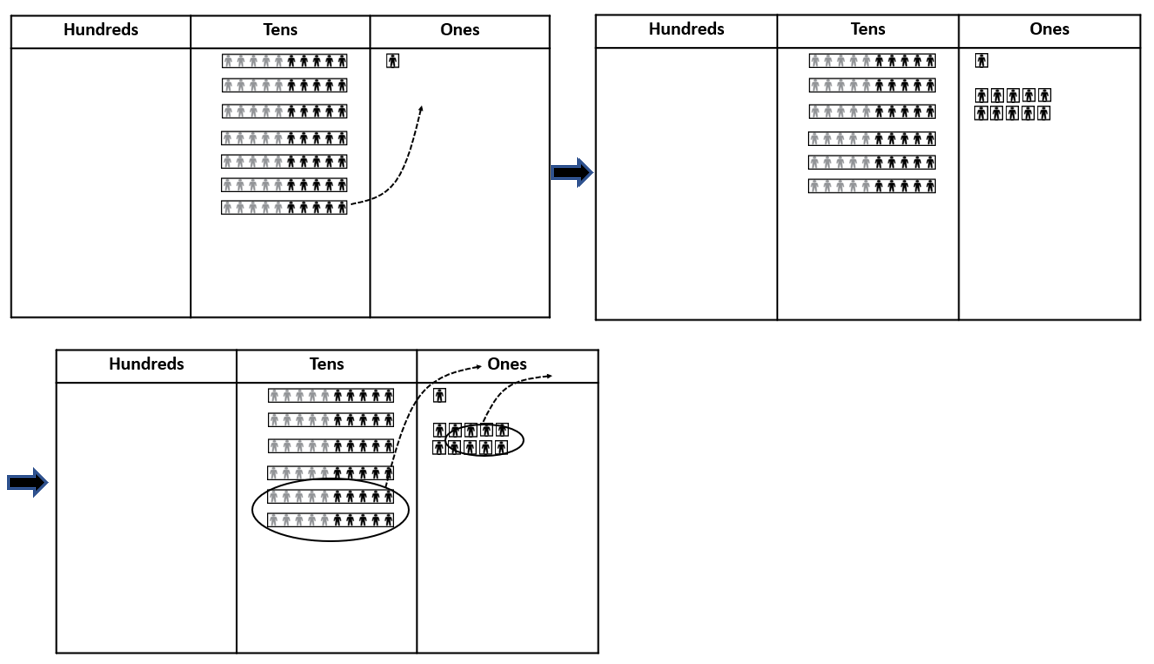
- Record the operation with an equation and an algorithm and make connections between the material and symbolic representations. Emphasise that the "sixty eleven" is found in the "6 11".
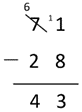 71 - 28 = 43
71 - 28 = 43
- Use a calculator so students know the sequence of pressing keys and to confirm the result.
- Provide other problems, altering the context as appropriate. Model each problem with materials (place value people and the three-column place value board), "back through" strategies on an empty number line, calculator sequences, equations, and a vertical written algorithm, as appropriate to the needs of your students. Look also for students to recognise the decomposition and renaming of a unit.
Subtracting two-digit numbers with renaming
- There are usually 64 students at the school. 36 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
Subtracting three-digit numbers with renaming (constrained to one place)
- There are usually 762 students at the school. 48 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
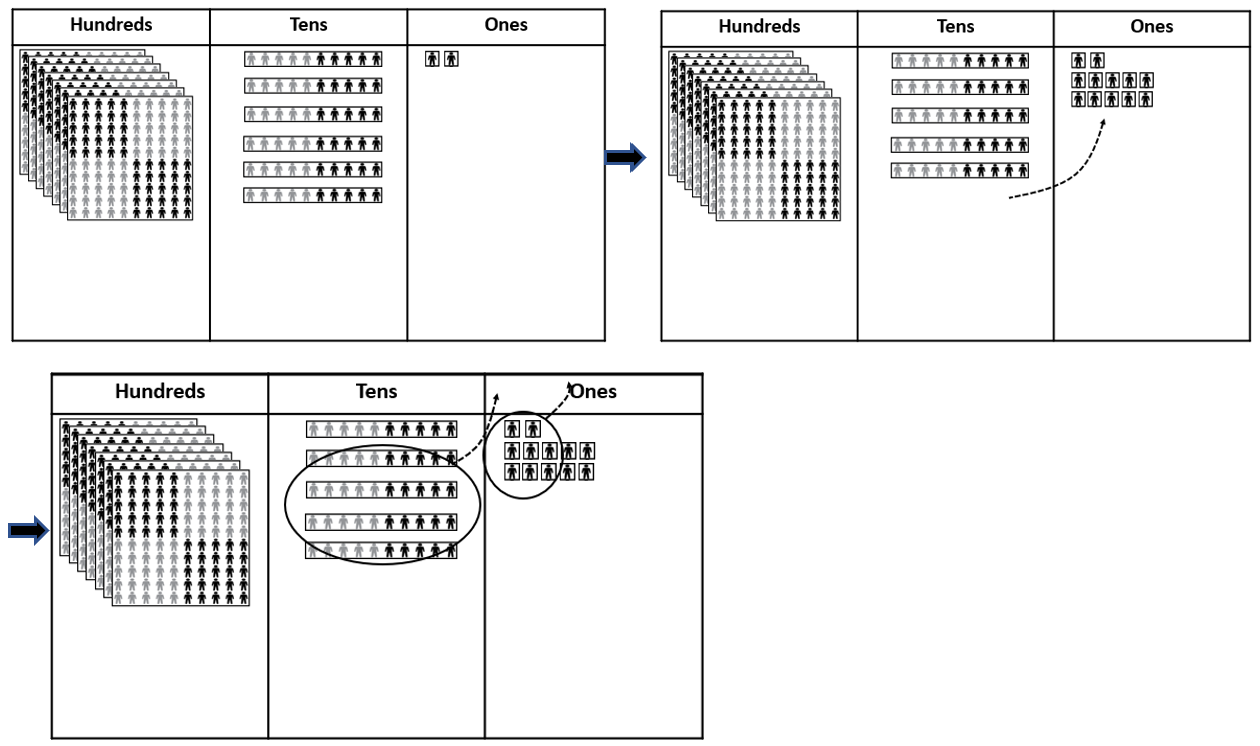
 762 - 48 = 714
762 - 48 = 714
Subtraction involving the decomposition of one hundred into ten tens
- There are usually 527 students at the school. 60 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
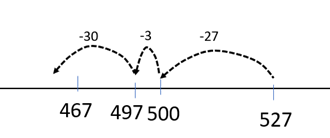
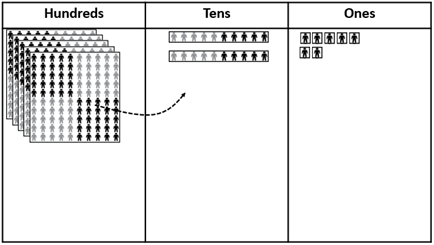
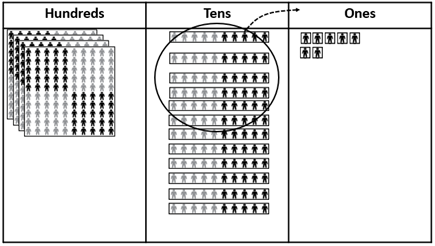
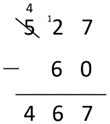 527 - 60 = 467
527 - 60 = 467
Subtraction involving the decomposition of one hundred or a ten
- There are usually 639 students at the school. 291 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
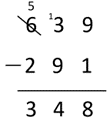 639 - 291 = 348
639 - 291 = 348
- There are usually 873 students at the school. 258 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
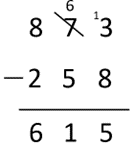 873 - 258 = 615
873 - 258 = 615
Next steps
- Progress to using algorithms and equations to solve problems using the same context. You might model the use of materials for the students as they solve the problem or support some students to "fold back" to the use of materials to check their working. Students should be provided with plenty of opportunities to develop fluency with subtraction strategies.
- Use the calculator to develop estimation strategies.
There are usually 965 students at the school. 482 students are away today with ill-health. How many students are at the school today?
Which answer is closest? 450, 460, 470, 480, 490, 500
How do you know?
Check with a calculator.