The purpose of this activity is to support students in solving addition problems with three-digit numbers, which involve ten ones combining to form a ten, or ten tens combining to form one hundred (renaming).
- Place Value People (a paper representation of hundreds, tens, and ones to be used by students)
- Scissors
- Calculators
- Three-column place value boards
- Pose initial problems with two-digit whole numbers, before progressing to problems with hundreds, tens, and ones. Use the context presented in the diagnostic question (or alter this to better reflect the interests and backgrounds of your class) and alter the numbers.
37 people are at the concert. 46 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?
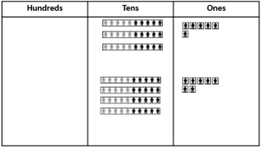
- Model the problem with Place Value People on a Place Value Board and provide time for students to discuss their thinking.
- What operation do you need to use? How do you know?
- How many tens do you have when you add the numbers?
- How many ones do you have when you add the numbers?
- Do you have enough ones to make another ten?
- Can you think of a similar problem that you could solve to help you solve this problem?
- Record the operation with an equation and an algorithm.
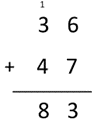 36 + 47 = 83
36 + 47 = 83
- Make connections between combining 6 + 7 = 13 to the meaning of the small 1 written in the tens column. For example: 6 + 7 = 13. To write13 I am going to work with the 3 and the 10 separately. I write 3 in the ones column and I write a small one above the tens column. The one shows that I am adding a ten to this column - the ten from 13. Now I can add up all the digits in the tens column to get the full answer.
Support students to see a connection between an extended expression of 36 + 47 (e.g. 30 + 40 + 10 + 3) and their basic facts knowledge (e.g. 3 + 4 + 1 = 80). You might demonstrate this using place value people and a calculator sequence.
- Provide other problems, altering the context as appropriate. Model each problem with materials (place value people and the three-column place value board), calculator sequences, equations, and a vertical written algorithm, as appropriate to the needs of your students.
Adding two-digit numbers with renaming
- 65 people are at the concert. 28 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?
Adding three-digit numbers - renaming ten ones into ten
- 346 people are at the concert. 237 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?
Look for students to recognise what unit the 1 in the tens column (i.e. the 10 in 13) refers to.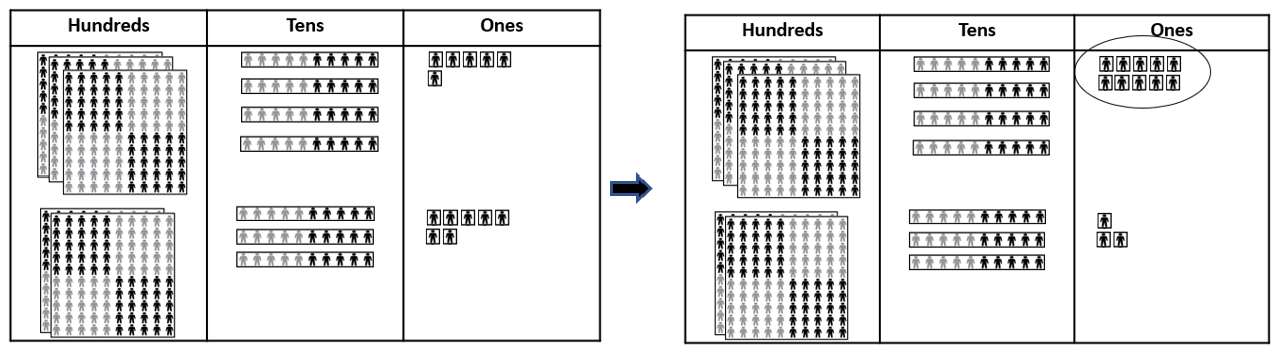
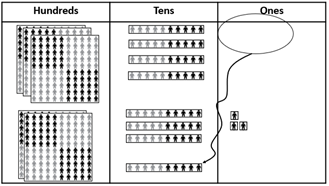
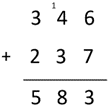 346 + 237 = 583
346 + 237 = 583
Adding three-digit numbers - renaming ten tens to form one hundred
- 562 people are at the concert. 185 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?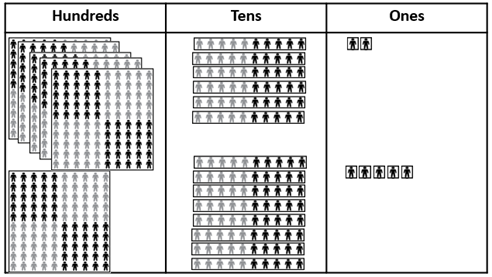
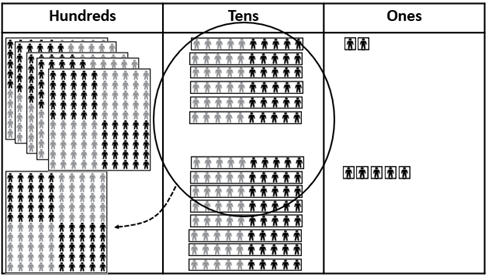
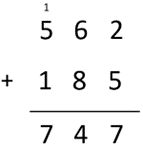 562 + 185 = 747
562 + 185 = 747
Adding three-digit numbers - renaming tens and ones
- 286 people are at the concert. 155 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?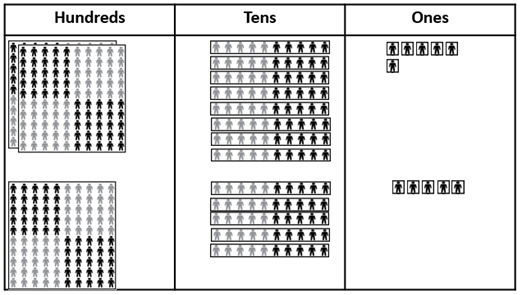
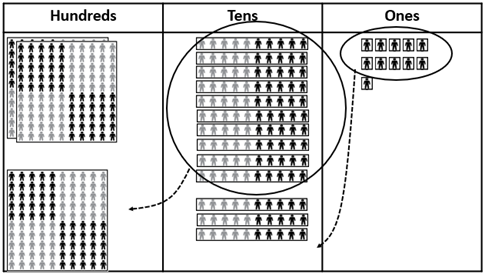
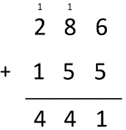 286 + 155 = 441
286 + 155 = 441
Next steps
- Progress to using algorithms and equations to solve problems in the same context. You might model the use of materials for the students as they solve the problem or support some students to "fold back" to the use of materials to check their working. Reinforce understanding with the use of calculator sequences and estimation strategies (e.g. that draw on students' tens and ones knowledge). For example:
Adding three-digit numbers - renaming ten hundreds to one thousand
- 642 people are at the concert. 623 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now? - 459 people are at the concert. 243 more people come along.
How many people are at the concert now?
Which answer is closest? 690, 700, 710, 720, 730
How do you know?
Check with a calculator.