The purpose of this activity is to support students in identifying the relative position of integers on a number line.
It is crucial that students integrate their knowledge of negative integers with their mental understanding of how a number line can be used to order, locate, and compare whole, positive numbers. The number line also develops the idea of an integer as a vector with either positive or negative direction and magnitude (length).
- Present students with an image of a thermometer showing a temperature below zero.
What does it mean to say the temperature is “minus 5 degrees”?
Students may know that in the Celsius scale, zero degrees (0⁰C) is the freezing temperature of fresh water. If possible, make links to a recent context in which the temperature has been below 0 degrees. Count the points on the thermometer scale to explicitly show that -5⁰C is five steps in the negative direction from zero. You might introduce relevant te reo Māori kupu within this discussion, such as paemahana (temperature) and tākiri (degree).
- Draw a vertical number line to represent a thermometer, and label in the middle 0 of it.
Use five negative integer cards or draw 5 arrows each representing -1 to show the position of -5. Continue to locate other temperatures like +5⁰C, -3⁰C, +1⁰C, and -10⁰C on the integer number line. You might do this in conjunction with finding out about the temperature of different cities from around the world.
- Ask students to create a horizontal integer number line using the integer cards.
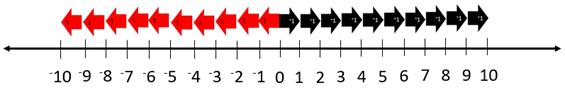
- Progress to imaging the position of numbers on the integer number line. Begin by only marking benchmark numbers like -10, 0, and 10, before locating other integers such as -2, 9, -7, and -11.
Where is 5 on this number line? (Students might jumps steps of positive one to find the location or halve the space between 0 and 10)
Where is -5 on this number line? (Students might jumps steps of negative one to find the location or halve the space between 0 and -10. They might also use symmetry and mark the position the same distance from zero as 5, in the negative direction).
- Have students play a few games of Integer Squeeze in pairs. The game works as follows:
- Each player starts by drawing several number lines to use for working. Alternatively you could use a laminated number line and whiteboard pens.
- Player A chooses an integer that is somewhere on the line.
- Player B has five chances to find the number by asking “is the number greater than …?” or “Is the number less than…?” questions.
- Discuss students’ strategies for playing the game and recording where the number might be.
- Player B: Is the number less than five (5)?
Player A: Yes
- Player B: Is the number greater than negative five (-5)?
Player A: Yes
Next steps
- Pose problems where students need to locate a specific integer on the line. Clues might include:
- I am greater than -8.
- I am less than zero.
- I am the same distance from zero as 6.
- Give students specific positions on integer number lines and ask them to name the number.
For example, what numbers are at positions A, B, C, and D?
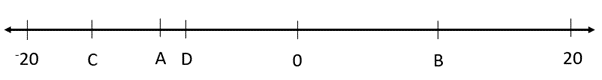
Look to see if students’ responses are consistent. For example, A and B have the same distance from zero. In mathematics we say that the absolute value of A and B are the same and write |A|=|B|. Since A is half-way between 0 and -20 it must be -10 and B must be 10.