Purpose
The purpose of this activity is to support students in reading, writing, and ordering decimals.
Achievement Objectives
NA4-6: Know the relative size and place value structure of positive and negative integers and decimals to three places.
Required Resource Materials
- Decimats (Material Master 7-3). Photocopy the decimats, staple five or six pages together, then cut them to size. Three decimats can be made from each sheet.
- Place value mat (photocopied to A3 size)
- Scissors
- Calculators
Activity
- Model different decimals with the decimats by organising the pieces in the correct position on the place value mat. Begin with using ones and tenths. For example:
Write the number 1.5
Can you read the number?
What does the five refer to in 1.5?
Use the place value mat to introduce the columns, ones, tenth, hundredths, and thousandths.
Make the number using decimats, and place the pieces in their correct position on the mat.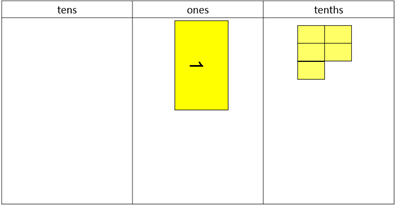
- Model the process of adding on tenths and naming the number that is created: 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9, and so on.
If I add tenths to 1.5 what do I get?
What happens when I add one tenth to 1.9? Why?
- Work with further numbers, involving ones and tenths, with an increasing expectation that students model the numbers and anticipate the result of one tenth being added or subtracted. Good examples might be:
3.4, 3.5, 3.6, ….
5.2, 5.1, 5, …
1.7, 1.6, 1.5, …
If needed, use a calculator to confirm counting patterns and predict further terms.
- Extend the numbers to include hundredths. For example:
Write 1.75.
Can you read the number?
What does the seven refer to? How do you know?
What column is the five in?
How are hundredths created? (Partitioning tenths into tenths)
Make 1.75 using decimats and locate the pieces on the place value mat.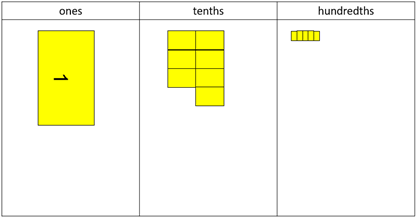
- As before, model the process of adding tenths and hundredths on to a number, this time containing hundredths (e.g. 1.75), naming the number created, and then confirming counting pattern on a calculator. For example: 1.75, 1.76, 1.77, 1.78, 1.79, and so on.
- Create numbers that have ones, tenths, hundredths, and thousandths. For example:
Write 2.386
Can you read the number?
What do the digits 3, 8 and 6 refer to?
How are thousandths created? (Equally partitioning hundredths into ten equal parts)
Make the number using decimats.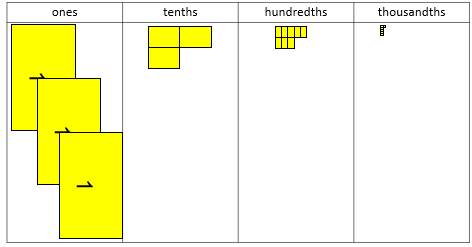
- Once the meaning of digits and decimat models are well established, pose ordering problems, such as:
Put these decimals in order from smallest to greatest
- 0.4
- 0.52
- 0.378
- Ask students to anticipate the order of the digits, then make a decimat model of each decimal to confirm the relative sizes.
Other examples might be:
- 1.098 1.1 1.09
- 2.6 2.54 2.078
These last two activities might by done in pairs to encourage tuakana-teina. Consider also whether some students will benefit from working independently, or from working more directly with the teacher.
Next steps
- Increase the level of abstraction by covering the materials, asking anticipatory questions, and working with more complex decimals.
- Develop place value understanding by asking students questions like:
What do I add to 0.482 to make 1?
What do I add to 1.63 to make it 1.9?
- Ask nested place value questions like:
How many hundredths are in all of 2.31?
How many thousandths are in all of 1.705?
Add to plan
Level Four