The purpose of this activity is to support students in developing their estimation skills in relation to expressing fractions as percentages.
- Connecting cubes
- Paper and pens
- Calculators
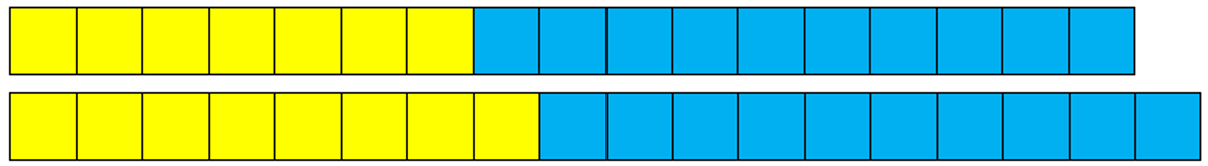
- Create a stack of 9 cubes, 5 yellow and 4 blue.
What fraction of this stack is yellow? What fraction is blue?
Estimate each fraction as a percentage.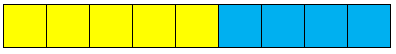
Students should recognise that the fraction of yellow is more than one half and the fraction of blue is less than one half.
Record 5/9 > 1/2 and 4/9 < 1/2. Estimates of more than 50% yellow and less than 50% blue are reasonable.
Use a calculator to find the actual percentages: 5 ÷ 9 % = 55.5% and 4 ÷ 9 % = 44.4%.
You might also express the fractions as decimals: 5/9 = 0.5 and 4/9 = 0.4.
- Make a stack of 13 cubes with 9 yellow and 4 blue.
What fraction of this stack is yellow? What fraction is blue?
Estimate each fraction as a percentage.
Is 9/13 more or less than three quarters?
Students might realise that 9/12 = 3/4 so the fraction of yellow is less than three quarters.
Record 9/13 < 3/4 .
What is a good estimate of 9/13? (Around 70% is reasonable since 3/4 = 75%)
Calculate the actual percentage using a calculator as 9 ÷ 13 % = 69.23% which is 0.6923…
What is a good estimate of 3/13?
Students should realise that, since 9/13 is less than three quarters, 4/13 must be more than 1/4. The fractions must add to one and the percentages to 100%.
4 ÷ 13 % = 30.77% which is 0.3077…
- Create further examples for students to practise estimating percentages. Allow students to work in groupings that will encourage peer scaffolding and extension, as well as productive learning conversations. Consider your students' fraction and multiplication basic facts knowledge when setting these problems. You might also introduce relevant te reo Māori kupu, such as ōrau (percent). Allow the use of a calculator to find the actual percentages once estimates are discussed. Good examples might include:
- What fraction of this stack is yellow? (11/16) What fraction is blue? (5/16)
Estimate each fraction as a percentage.
5/16 > 4/16 = 1/4 so a bit more than 25% is a good estimate
11/16 < 12/216 = 3/4 so a bit less than 75% is a good estimate or subtract the estimate for 5/16 from 100%.
- What fraction of this stack is yellow? (8/19) What fraction is blue? (11/19)
Estimate each fraction as a percentage.
8/19 > 8/20 = 2/5 so a bit more than 40% is a good estimate
11/19 is about 12/20 = 3/5 so 60% is a good estimate or subtract the estimate for 8/19 from 100%.
- What fraction of this stack is yellow? (8/23) What fraction is blue? (15/23)
Estimate each fraction as a percentage.
8/23 > 8/24 = 1/3 so a bit more than 33% is a good estimate
15/23 < 16/24 = 2/3 so a bit less than 66% is a good estimate or subtract the estimate for 8/23 from 100%.
- What fraction of this stack is yellow? (11/16) What fraction is blue? (5/16)
Next steps
- Increase the level of abstraction with the aim of students using symbolic form. Start with stacks of discrete numbers of cubes, before progressing to schematic diagrams with only the number of cubes given:

Use symbolic form to express the fractions as 12/25 and 13/25. This can then be converted to percentages by scaling to 100.
25 multiplied by four equals 100 so 12/25 = 48/100 = 48% and 13/25 = 52/100 = 52%.
- Ask students to demonstrate with stacks of cubes what the use of rounding means in an estimation situation. For example, estimating 7/17 and 10/17 by changing into 6/18 = 1/3 and 12/18 = 2/3 involves increasing the number of cubes in the stack by one. Each eighteen is less than each seventeen but that is compensated by adding one to the numerator. It is better to make stacks for the original fraction and the modified fraction separately so they can be compared. For example, 7/17 and 8/18 look like this: