This is a level 3 number activity from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 6 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is available.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (473 KB)
use arrays to solve multiplication facts
FIO, Level 3, Number, Book 2, Movie Maths, page 6
A classmate
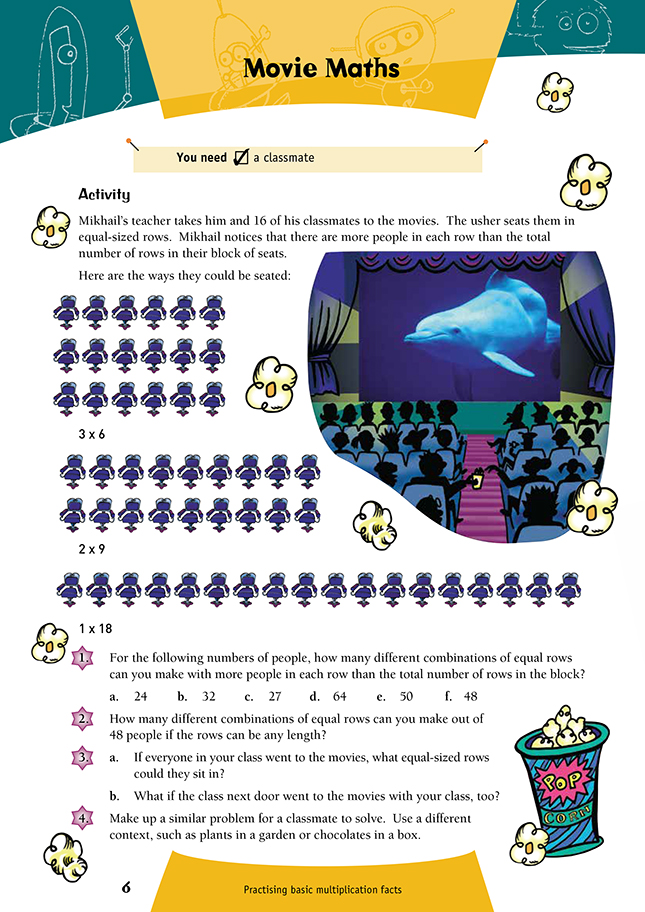
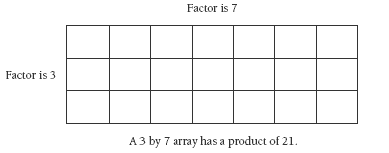
The context for this activity was chosen so that students would connect the array structure in the seating with multiplication. The sides of the array are the factors, while the total number of seats is the product.
The ability to visualise multiplication as an array pattern is vital for interpreting many problems. It also enables the students to work out multiplication facts before they have committed them to memory.
Question 1 is based on the fact that Mikhail notices that there are more people in the row than there are rows. This reduces the choice of arrays. For example, they can sit in 3 lots of 6 people in a row but not in 6 lots of 3 in a row.
In question 2, this restriction is removed, so all the combinations of 2 factors that make 48 need to be shown.
In question 3, which is an open-ended question, the students practise seeing the arrays as factors and multiples. It may also present an opportunity to look at prime numbers. For example, if 29 children are in the class, the only array is 29 people in 1 row. This is a nice way to visualise a prime number.
Question 4 is important because it encourages the students to generalise the array notion of multiplication by choosing other contexts that have that structure. This generalisation is their key to recognising types of problems that can be solved by multiplication. Ensure that this point is made explicit at the conclusion of the activity.
Answers to Activity
Activity
1. a. 4 different combinations. (1 x 24, 2 x 12, 3 x 8, 4 x 6)
b. 3 different combinations. (1 x 32, 2 x 16, 4 x 8)
c. 2 different combinations. (1 x 27, 3 x 9)
d. 3 different combinations. (1 x 64, 2 x 32, 4 x 16)
e. 3 different combinations. (1 x 50, 2 x 25, 5 x 10)
f. 5 different combinations. (1 x 48, 2 x 24, 3 x 16, 4 x 12, 6 x 8)
2. 10 different combinations. (1 x 48, 2 x 24, 3 x 16, 4 x 12, 6 x 8, 8 x 6, 12 x 4, 16 x 3, 24 x 2, 48 x 1)
3. a.–b. Answers will vary.
4. Answers will vary.