Change start-unknown problems to change-unknown problems.
Solve addition and subtraction problems by compensating with tidy numbers.
Number Framework Stage 5
Number Lines (Material Master 5-12)
Students need to develop an understanding of place-value mental strategies by using equipment that allows for grouping as well as a continuous model such as a number line. The number line model preserves the magnitude of a number and shows where it fits among other numbers. It also provides a strong image for students to work with and is particularly useful for solving subtraction problems.
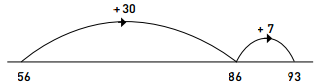
Addition and subtraction on a number line involve keeping the first number whole and partitioning the second. For example, 56 + 37 = ? can be solved in the following way:
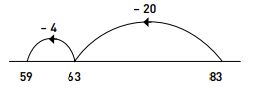
Likewise, on a number line, 83 – 24 = ? can be shown as:
Step 1: 83 – 20 = 63
Step 2: 63 – 4 = 59
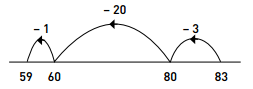
Alternatively:
Step 1: 83 – 3 = 80
Step 2: 80 – 20 = 60
Step 3: 60 – 1 = 59
Using materials
Problem: On sports day, there were fifty-seven senior students and forty-five junior students competing in different events. How many students were competing altogether at the sports day?
Have the students solve the problem by using empty number lines.
Ask: “How might you show this problem on a number line?” Record strategies on the board or in the modelling book.
Examples: Word problems and recording for: 68 + 26, 37 + 24, 158 + 46, 72 – 34, 143 – 26, 251 – 33 …
Using imaging
Students rely on the number line image to support their thinking.
Examples: Word problems and recording for: 85 – 56, 78 + 27, 86 + 47, 42 – 25 …
Using number properties
Students can jot down a number to support short-term memory.
Examples: Word problems and recording for: 528 – 86, 728 + 34, 456 + 127, 563 – 125 …