Prior knowledge.
Write a whole number in expanded form
Explain the role of the decimal point as separator of the wholes and the parts of a whole
Write tenths and hundredths in decimal and fraction form
Background
It is important that students develop a good sense of understanding of decimal palce value.
Comments on the Exercises
Exercise 1
Asks students to write a number in expanded form.
Exercise 2
Asks students to write the expanded number as a one decimal place number.
Exercise 3
Asks students to colour in the decimal (tenths decimals and hundredths decimals) on a diagram.
Exercise 4
Asks students to write mixed number fractions with a 100 as a denominator as a decimal. For example, 15/100 = 0.15.
Exercise 5
Asks students to underline the digit in the hundreds place.
Exercise 6
Asks students to circle around the digit in the hundredths place.
Exercise 7
Asks students to add one hundredth (1/100) to numbers.
Exercise 8
Asks students to subtract one hundredth (1/100) from numbers.
Exercise 9
Asks students to add one hundredth (0.01) to decimal numbers.
Exercise 10
Asks students to subtract one hundredth (0.01) to decimal numbers.
Exercise 11
Asks students to identify the digit in the tens, hundreds, tenths, hundredths column in numbers.
Exercise 12
Asks students to identify what number an arrow is pointing to a decimal number line. This exercise taps into the measure construct of decimals, so may be harder for students to work with than the numbers alone. This is because number lines use a different set of conventions to those used in counting. For example, in this exercise it is important for students to start off by looking at the numbers at each end of the interval, then working out what each major mark, and each minor mark stands for. It is surprising how many students assume that each (major) mark stands for one, with each of the little marks being a tenth, and do not realise that they need to start out by identifying the scale on the interval.
Exercise 13
Asks students to multiply hundredths in the form of 6 lots of 2/12. This activity introduces students to multiplication of fractions, but uses the more familiar concepts of ‘lots of’. Introductory problems can be modelled using equipment like decipipes or place value blocks before the exercise is introduced. The final problems involve students writing and marking their own problems, including one word problem. This latter should be collected in for marking, to check that students have developed an understanding of the multiplications, and can recognise an instance in which using this process would be of value. Discussing the word problems may be an important follow-up, especially where some students have demonstrated lack of understanding. Modelling what they have created as a problem with materials would be a useful way of correcting misconceptions about which practical problems utilise this skill.
Exercise 14
Asks students to multiply by hundredths in the form of 0.03 x 4. This exercise looks at multiplication of decimals. Note that the standard algorithm will cause some students grief (for example 0.06 x 5 = 0.3, which does not have two decimal places). Again, this topic should be introduced using equipment like decipipes or place value blocks to build an understanding of the process. Using language like 4 lots of three hundredths equals twelve hundredths (and how do we write this) is useful.
Place Value Practice (Tenths)
These exercises and activities are for students to use independently of the teacher to practice number properties.
write a decimal in expanded form, and vice versa
shade in tenths
identify digits in the tenths column
convert improper fractions involving tenths to both a mixed number and a decimal
add and subtract a tenth from a number
identify a number on a number line marked in tenths
Number Sequence and Order, AA (Stage 6)
Prior knowledge.
Background
It is important that students develop a good sense of understanding of decimal palce value.
Comments on the Exercises
Exercise 1
Asks students to write a number in expanded form using fractions. For example, 34.5 = 30 + 4 + 5/10
Exercise 2
Asks students to write the expanded number as a one decimal place number.
Exercise 3
Asks students to colour in the decimal tenths on a diagram. For example, 0.7.
Exercise 4
Asks students to write mixed number fractions with a 10 as a denominator as a decimal. For example, 23/10 = 2.3.
Exercise 5
Asks students to underline the digit in the tenths place.
Exercise 6
Asks students to circle around the digit in the tens place.
Exercise 7
Asks students to add one tenth to decimal numbers.
Exercise 8
Asks students to subtract one tenth from decimal numbers.
Exercise 9
Asks students to identify the digit in the tens place and in the tenths place.
Exercise 10
Asks students to identify what number an arrow is pointing to on a decimal number line.
Related activities
Place Value Practice (Tenths and Hundredths)
These exercises and activities are for students to use independently of the teacher to practise number properties.
Number Sequence and Order, AA-AM (Stage 6 -7)
Prior knowledge.
Write a whole number in expanded form
Explain the role of the decimal point as separator of the wholes and the parts of a whole
Write tenths and hundredths in decimal and fraction form
Background
It is important that students develop a good sense of understanding of decimal palce value.
Comments on the Exercises
Exercise 1
Asks students to write a number in expanded form.
Exercise 2
Asks students to write the expanded number as a one decimal place number.
Exercise 3
Asks students to colour in the decimal (tenths decimals and hundredths decimals) on a diagram.
Exercise 4
Asks students to write mixed number fractions with a 100 as a denominator as a decimal. For example, 15/100 = 0.15.
Exercise 5
Asks students to underline the digit in the hundreds place.
Exercise 6
Asks students to circle around the digit in the hundredths place.
Exercise 7
Asks students to add one hundredth (1/100) to numbers.
Exercise 8
Asks students to subtract one hundredth (1/100) from numbers.
Exercise 9
Asks students to add one hundredth (0.01) to decimal numbers.
Exercise 10
Asks students to subtract one hundredth (0.01) to decimal numbers.
Exercise 11
Asks students to identify the digit in the tens, hundreds, tenths, hundredths column in numbers.
Exercise 12
Asks students to identify what number an arrow is pointing to a decimal number line. This exercise taps into the measure construct of decimals, so may be harder for students to work with than the numbers alone. This is because number lines use a different set of conventions to those used in counting. For example, in this exercise it is important for students to start off by looking at the numbers at each end of the interval, then working out what each major mark, and each minor mark stands for. It is surprising how many students assume that each (major) mark stands for one, with each of the little marks being a tenth, and do not realise that they need to start out by identifying the scale on the interval.
Exercise 13
Asks students to multiply hundredths in the form of 6 lots of 2/12. This activity introduces students to multiplication of fractions, but uses the more familiar concepts of ‘lots of’. Introductory problems can be modelled using equipment like decipipes or place value blocks before the exercise is introduced. The final problems involve students writing and marking their own problems, including one word problem. This latter should be collected in for marking, to check that students have developed an understanding of the multiplications, and can recognise an instance in which using this process would be of value. Discussing the word problems may be an important follow-up, especially where some students have demonstrated lack of understanding. Modelling what they have created as a problem with materials would be a useful way of correcting misconceptions about which practical problems utilise this skill.
Exercise 14
Asks students to multiply by hundredths in the form of 0.03 x 4. This exercise looks at multiplication of decimals. Note that the standard algorithm will cause some students grief (for example 0.06 x 5 = 0.3, which does not have two decimal places). Again, this topic should be introduced using equipment like decipipes or place value blocks to build an understanding of the process. Using language like 4 lots of three hundredths equals twelve hundredths (and how do we write this) is useful.
Related activities
Jumping the number line – decimal fractions (hundredths)
These exercises and activities are for students to use independently of the teacher to practice number properties.
Using jumping the number line strategy to add decimal fractions (tenths and hundredths).
Addition and subtraction, AM (Stage 7)
Prior knowledge.
Background
In this activity students use additive strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems involving decimals. Students need to have a good understanding of place value to make sense of the strategies with decimals.
Comments on the Exercises
Exercise 1
Asks students to solve problems by jumping a whole number and then a decimal. For example, 6 + ? = 8.55, 6 + 2 = 8, 8 + 0.55 = 8.55 so the answer is 2.55.
Exercise 2
Asks students to solve problems by jumping to the nearest whole number, then the next whole number and then make a decimal jump. For example, 4.97 + ? = 8.12, jump 0.03 to 5, then 3 from 5 to 8, then 0.12 to 8.12
Exercises 3 and 4
Asks students to reduce the number of jumps they used in Exercise 2. For example, 3.98 + ? = 9.3, jump 0.02 to 4 then 5.3 to 9.3.
Exercise 5
Asks students to choose their own strategy to solve problems like 11.82 + ? = 38.3.
Exercises 6 and 7
Asks students to solve problems like in Exercise 5 but the numbers are larger, for example 19.88 + ? = 224.52
Written recording
Written recording of mental strategies (that is, how you thought through the problem) is important for developing sound assessment skills as it allows others to follow your reasoning and allows you to have a visual check for accidental errors. It is also something that develops over time, and needs to be discussed regularly with students. Exercises 5, 6 and 7 stress that students should solve the problems mentally, but record enough to show what they have done. Discussing or eliciting different ways of doing this is therefore an important activity, which you may choose to run either before or after setting students to work on this exercise
Deci-order
This activity provides students with a fun, game context in which to practice their decimal number ordering skills.
use their knowledge of the number system to create the biggest decimal number.
Gameboard
Extension
Increase the numbers beyond the decimal place. To do this you will need to allow more cards in the pack.
My Decimal Number
In this activity students brainstorm different ways to represent decimal fractions. They will draw on their knowledge of decimal place value, addition and subtraction of decimals, and writing decimals in words and symbols.
represent decimal numbers in a variety of ways
For example 3.81 could be expressed as;
Decimal Calculator Numbers
The purpose of this activity is to work out a hidden number on a calculator using knowledge of number sequence.
use their knowledge of decimal number sequence order decimals.
Decimal Day
This is a level 4 number activity from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 7 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (232 KB)
order decimals to 2 decimal places
This activity focuses on ordering decimals to two places. Students could model the height of each player using two metre rulers on the floor.
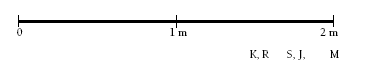
K, R, S, J, and M are the initial letters of the players.
Introduce question 2 carefully. Students may have difficulty fully understanding the question. They need to be clear who is in the original team and who the new players are. Read it through with the students. Highlight the team changes by asking: “Who are the two new players? Who must have been left out if Aroha is now the shortest?”
Game
This game is short and simple but very effective for challenging students’ understanding of the digits involved in decimal numbers.
Have the winning students justify their result by talking about the place value of their digits. Vary the rules to create more learning opportunities. For example, you could ask students to “Make the largest decimal with a two-digit whole number in it. Make the smallest decimal with a one-digit whole number in it. Make the biggest number you can that is smaller than 7 but larger than 3.9.”
Answers to Activity
1. Centre: Minnie (tallest)
Guards: Joe and Stretch (second and third tallest)
Forwards: Ruth and Kevin (shortest)
2. a. Joe and Stretch
b. Joe is a guard, and Stretch is a forward.
c. Ruth and Kevin
Game
A game using decimals