This is a level 2 algebra strand activity from the Figure It Out series.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (320 KB)
use <, >, = symbols in equations
Activity One
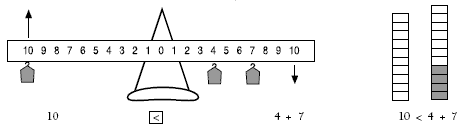
Some students may find the examples of inequalities in this activity difficult, and they will need prior experience with simpler inequalities, for example, 10 4 + 7. Physical models, such as number balances and towers of connecting cubes, can help develop the students’ understanding.
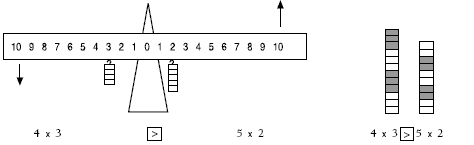
These models still apply when each side of an inequality contains an operation, for example, 4 x 3 5 x 2.
Students need to have the ability to process operations as mental ideas and understand the equals sign in order to cope with inequalities. For example, the student who has 4 + 7 = 11 as an idea in their mind without having to calculate it with equipment or mentally is much better prepared to solve the inequality 13 4 + 7. The ability to process inequalities mentally is the aim of these activities; manipulation of equipment is a means towards that end.
Activity Two
This activity involves the students being able to interpret a flow chart for grouping children for swimming lessons. Students could be “walked through” how the flow chart works, using the example of actual students from their class. As an extension, students may like to create a flow chart about sorting a set of attribute blocks into triangles, squares, hexagons, and circles.
Answers to Activities
Activity One
1. a. =
b. <
c. 7 or higher
d. >
e. <
f. 1 or 0
g. >
h. 4 or more
2. Answers will vary. They could include:
“I worked out the numbers on each side of the symbol and then decided which symbol (<, >, or =) to use.”
3. Answers will vary.
Activity Two
1. Tama belongs to Sharks.
2. Va‘e belongs to Dolphins.
3. Jesse belongs to Sea horses.
4. Rama belongs to Sharks.