Inside Irregular Polygons
The purpose of this activity is to engage students in using a given rule, to deduce another rule. This is an example of the deductive reasoning required for forming successful geometric proofs.
This activity assumes the students have experience in the following areas:
- Measurement of angles.
- Properties of common polygons.
- Sum of interior angles of triangles.
- Continue and find the general rule for linear relationships.
The problem is sufficiently open ended to allow the students freedom of choice in their approach. It may be scaffolded with guidance that leads to a solution, and/or the students might be given the opportunity to solve the problem independently.
The example responses at the end of the resource give an indication of the kind of response to expect from students who approach the problem in particular ways.
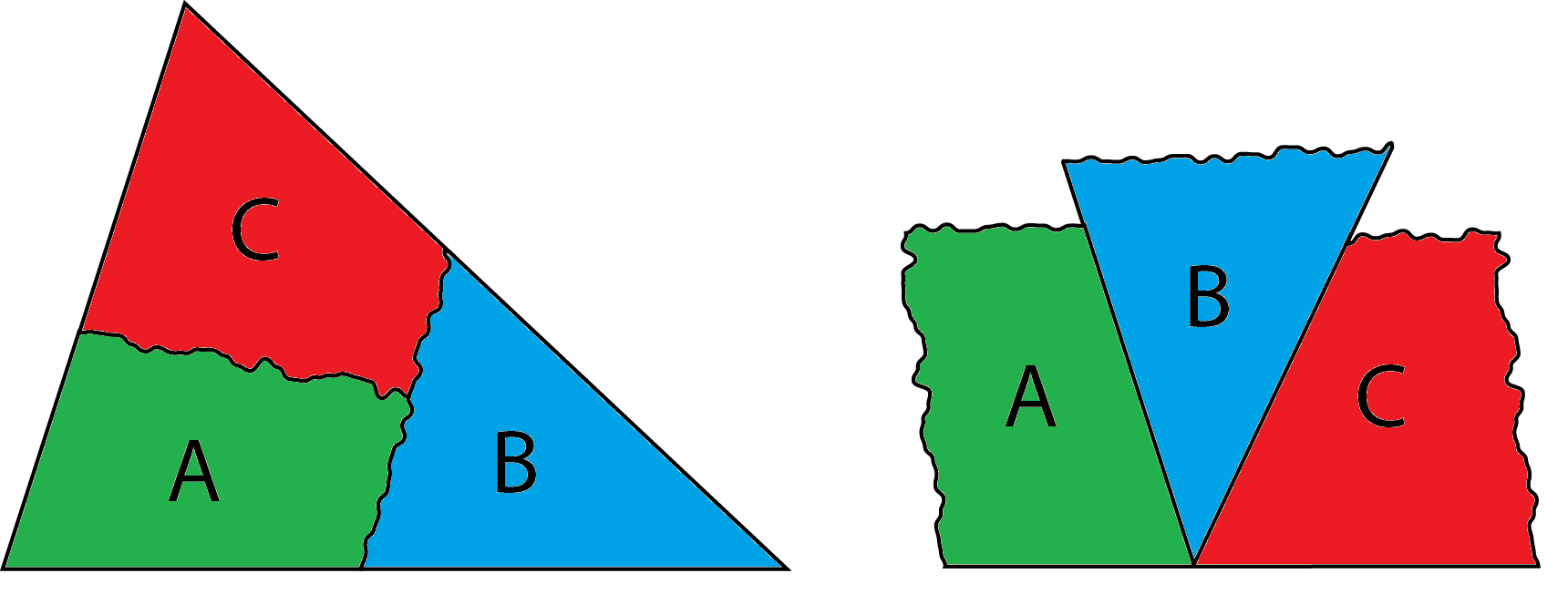
Task: To show that the sum of the internal angles of any triangle is 180°, a triangle can be torn into three parts so that the three internal angles can then be lined up. Use this practical idea, to find a relationship, or rule, between the number of sides of any polygon and the sum of its internal angles.
The following prompts illustrate how this activity can be structured around the phases of the Mathematics Investigation Cycle.
Make sense
Introduce the problem. Allow students time to read it and discuss in pairs or small groups.
- Can I rephrase the problem in my own words?
- Can I imagine (visualise) what tearing off the angles, and positioning them around a point, looks like?
- Does this look/sound like a problem I have worked on before? (Has the student measured interior angles of polygons using a protractor?)
- What information has been given?
- Is all this information needed?
- What will a generalisation about interior angles look like?
- How will the generalisation be expressed?
Plan approach
Discuss ideas about how to solve the problem. Emphasise that, in the planning phase, you want students to say how they would solve the problem, not to actually solve it.
- What are the maths skills I need to work this out? (Students will need to know about the meaning of angles and how to measure angles in degrees.)
- What could the solution be? (A generalisation will connect the number of sides or angles of a polygon with the sum of interior angles.)
- What strategies can I use to get started? (Practically joining angles of different polygons around a point.)
- What will I need to record as I work? (A table make help coordinate data and support pattern seeking.)
- What tools (digital or physical) could help my investigation? (Calculators and protractors will be helpful.)
Take action
Allow students time to work through their strategy and find a solution to the problem.
- Have I shown my workings in a step-by-step way?
- How can we share the mahi in our group to get the best result?
- Does my data seem correct when I compare it to that of other students?
- Is there a pattern? (Sum of interior angles increases by 180 with the addition of an extra side to the polygon.)
- Is there a way to express the pattern, that I see, as a general rule?
- Can I use algebra to record my rule?
Convince yourself and others
Allow students time to check their answers and then either have them pair share with other groups or ask for volunteers to share their solution with the class.
- What is the generalisation?
- Have I checked my rule with many examples (cases)?
- Can others see how I worked it out? Is my investigation process clear?
- How will I convince others that my rule is correct?
Examples of work
Work sample 1
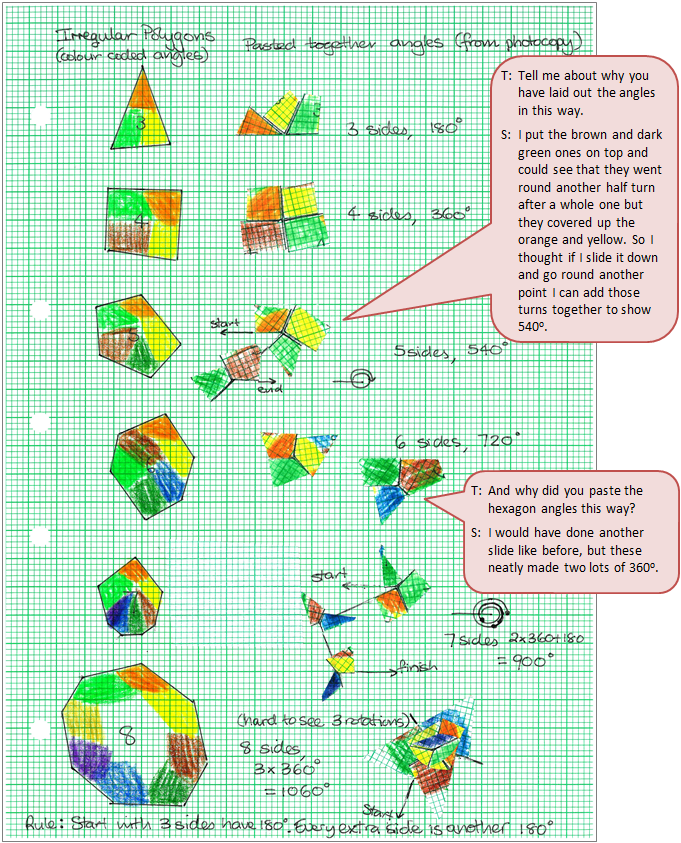
The student finds a pattern that leads to a rule, using practical exploration.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close.
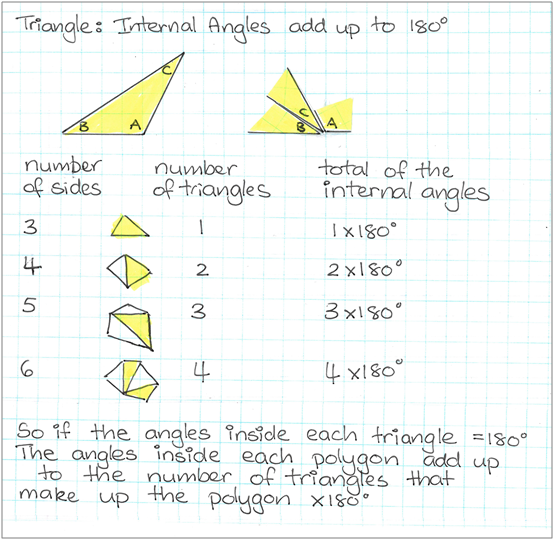
Work sample 2
The student builds the angle sums of polygons in a sequential way, using practical exploration to generalise the rule for sum of interior angles, with guidance.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close.
Work sample 3
The student builds the angle sums of polygons in a sequential way, using practical exploration to generalise the rule for sum of interior angles, independently.