Estimate and find percentages of whole number and decimal amounts.
Number Framework Stage 8
Reverse Percentage Problems (Material Master 8-32)
Students with poor understanding of the meaning of percentages find inverse percentage problems impossible. For example, finding the pre-discount price when, after a 15% discount, a TV costs $350 is a challenging problem. Problems like this are easier to solve when percentages are converted to decimals before calculation.
Using Materials
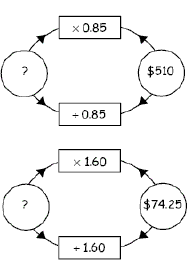
Problem: “Pare receives a 15% discount on a TV, and he pays $510. What was the price before the discount?”
Draw an empty flow chart on the board. Discuss why the unknown full price is multiplied by 0.85.
Discuss why the full price is found by division, and have the students calculate this price. (Answer: 510 ÷ 0.85 = $600.)
Problem: “Melissa buys blouses for her clothes store. She marks the price up by 60%. If she sells a blouse for $74.25, how much did the blouse cost her?” Discuss why the flow chart shows that the cost price was 74.25 ÷ 1.60 = $46.41 (to the nearest cent).
Using Imaging
Problem: “Janice adds GST of 15% to the price of a toaster. It now costs $31.50. What was the price of the toaster before GST was added?”
Imagine the flow chart and reverse it to find the answer.(Answer: $31.50 ÷ 1.15 = $27.39.)
Examples: Image flow charts. Fold back to drawing them if needed. Worksheet (Material Master 8–31).
Using Number Properties
Examples: Worksheet (Material Master 8–32).
Understanding Number Properties:
k% of the selling price $p is profit. What is the cost price?
(Answer: $p(100-k) / 100 .)