This is a level 4 number link activity from the Figure It Out series. It relates to Stage 7 of the Number Framework.
A PDF of the student activity is included.
Click on the image to enlarge it. Click again to close. Download PDF (167 KB)
show understanding of decimal place value
Decimal Compact Numeral Cards (see Copymaster)
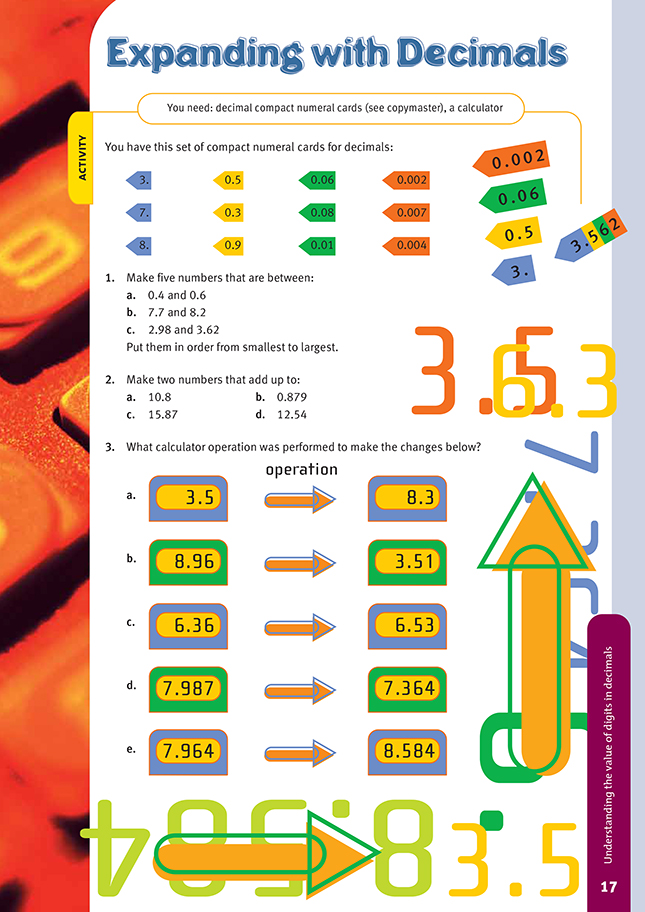
FIO, Link, Number, Book Two, Expanding with Decimals, page 17
A calculator
A copymaster of decimal compact numeral cards is provided at the end of these notes.
This activity builds on the last activity by introducing decimals. Note that the arrows are now on the left side so that the digits can be aligned from the ones place. Note also that the card with the smallest number (which has the most digits) goes on the bottom when a compact numeral is made.
Question 1 challenges students’ perceptions of the relationship between the number of digits and the size of decimal numbers. Many students judge the size of numbers by the number of digits they contain. This will lead to misunderstandings because a one-digit decimal can be larger than a three-digit decimal. Ask the students “What do you look for to judge the size of a decimal number?” A good response would indicate that the first significant digit to the right of the decimal point is a useful place to start (for example, the 2 in 57.23).
Point out to your students that the job of the decimal point is to indicate the position of the ones place. They can then ascertain the value of all other digits. Make sure that the students do not use a column space for the decimal point. If they do, they often lose the relationship between the ones place and the tenths place.
In question 3, the students could approach the comparisons as difference questions initially to find the quantity involved. They could then look at the relationship suggested by the arrow to see if the quantity should be added or subtracted.
Answers to Activity
1. Answers will vary. You should have five out of each of the following, in the order listed.
a. 0.5, 0.51, 0.512, 0.514, 0.517, 0.56, 0.562, 0.564, 0.567, 0.58, 0.582, 0.584, 0.587
b. 7.9, 7.91, 7.912, 7.914, 7.917, 7.96, 7.962, 7.964, 7.967, 7.98, 7.982, 7.984, 7.987, 8.01, 8.012, 8.014, 8.017, 8.06, 8.062, 8.064, 8.067, 8.08, 8.082, 8.084, 8.087
c. 3, 3.002, 3.004, 3.007, 3.01, 3.012, 3.014, 3.017, 3.06, 3.062, 3.064, 3.067, 3.08, 3.082, 3.084, 3.087, 3.3, 3.302, 3.304, 3.307, 3.502, 3.504, 3.507, 3.31, 3.312, 3.314, 3.317, 3.36, 3.362, 3.364, 3.367, 3.38, 3.382, 3.384, 3.387,
3.5, 3.51, 3.512, 3.514, 3.517, 3.56, 3.562, 3.564, 3.567, 3.58, 3.582, 3.584, 3.587
2. a. 7.5 + 3.3 or 7.3 + 3.5
b. 0.567 + 0.312, 0.562 + 0.317, 0.517 + 0.362, or 0.512 + 0.367
c. 8.56 + 7.31, 8.51 + 7.36, 8.36 + 7.51, or 8.31 + 7.56
d. 3.56 + 8.98, 3.58 + 8.96, 3.96 + 8.58, or 3.98 + 8.56
3. a. + 4.8
b. – 5.45
c. + 0.17
d. – 0.623
e. + 0.62